what do rods do in the eye
Quarterfreelp and 2 more users found this answer helpful. Cones are responsible for color vision.
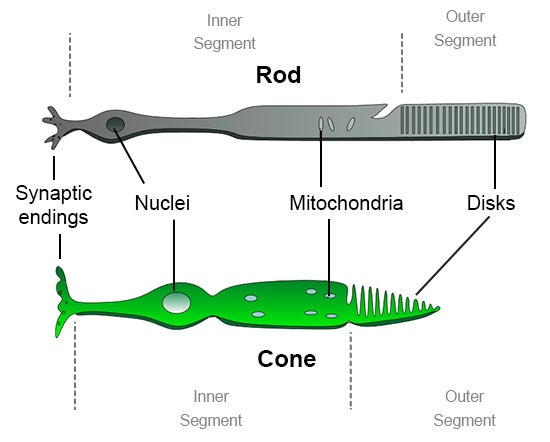
How Do We See Light Ask A Biologist
Rods are a part of the eye that takes in low light.
. Rods are responsible for vision at low light levels scotopic vision. Rod cells or rods are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in less intense light than can the other type of photoreceptor cone cells. Because they are more light sensitive rods are responsible for night vision.
They are concentrated in the outer areas of the retina and give us peripheral vision. And these are just fun facts about eyes. They are only responsible for light and dark.
This is why you are still able to perceive shapes and some objects even in dim light or no light at all. Rods and cones are light-sensitive cells in the retina. Download PDF Contribution of.
These rods are responsible for night vision our most sensitive motion detection and our peripheral vision. They gather the information you see so that it may be transferred to and interpreted by the brain. Rods are concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision.
What do rods do in the eye. They do not mediate color vision and have a low spatial acuity. Cones require a lot more light and they are used to see color.
On average there are 120 million rods in the human eye which are more than a thousand times as sensitive as individual cones. Rods are a part of the eye that takes in low light. Rod cells or rods are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in less intense light than the other type of visual photoreceptor cone cells.
On the other hand the rods are absent from the fovea. All mammals have rods and cones in their eyes. Where is retinal disparity located.
Smoking reduces your night vision. They do not perceive colour and fine detail tasks performed by the other major type of light-sensitive cell the cone. However rods do not perceive color.
Rods work at very low levels of light. Rods pick up signals from all directions improving our peripheral vision motion sensing and depth perception. Rods and cones are the receptors in the retina responsible for your sense of sight.
Cones are located in the retina and they are responsible for seeing in color. Named for their cylindrical shape rods are concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. They are usually on the outer edges of the retina and they are mostly used in peripheral vision.
Finally the timing of the evolution of cone and rod photoreceptors the retina and the camera-style eye is summarised. The rods and cones are responsible for detecting light and are properly referred to as Photoreceptors. Rods are connected in groups to ganglion cell and if enough light above threshold hits any cells in the group then they get nerve impulses to brain along the optic nerve.
These are 500 to 1000 times more responsive to light than cones making them ideal for providing vision in dim conditions. Cones are active at higher light levels photopic vision are capable of color vision and are responsible for high spatial acuity. There are two types of photoreceptors in the human retina rods and cones.
Rod cells are stimulated by light over a wide range of intensities and are responsible for perceiving the size shape and brightness of visual images. We use these for night vision because only a few bits of light photons can activate a rod. Cones are located in the retina and they are responsible for seeing in color.
Rods dont help with color vision which is why at night we see everything in a gray scale. Rods are a type of photoreceptor cell in the retina. It takes your eyes time to adjust from a well-lit room to a dark room or if youre outside during nighttime.
When stimulated they generate electrical impulses which pass to the brain along the optic nerve. The Journal of Neuroscience 2018. The rods and cones in the eye are the bodys sensory equipment in the back of the eye.
Rod cells in the eye are photoreceptor cells that are located in the retina of the eye and have the ability to function with a lower light intensity than the other photoreceptor cells called cone cells. Rods are very sensitive to light but do not distinguish colors. They are the part of the eye responsible for converting the light that enters your eye into electrical signals that can be decoded by the vision-processing center of the brain.
The rod is responsible for your ability to see in low light levels or scotopic vision. The retina has approximately 120 million rods and 6 million cones. The rod is more sensitive than the cone.
Rods are located away from the center of the retina the term retina is not required and are responsible for peripheral vision. The normal retina has rods that see only black white and shades of grey and tones and three forms of color cones red green and blue. Continue Learning about Eye and Vision.
They are located on the outside area of the retina. It is not enough merely to say that rods allow us to detect movement and form or to see in dim light or in black and white because the question specifies peripheral vision. There are 120 million light-sensing cells called rods which help you to see better in the dark.
Rods are 500 to 1000 times more sensitive to light than cones. At a few degrees away from it their density rises to a high value and spreads over a large area of the retina. There are many rods in other parts of the retina.
All mammals have rods and cones in their eyes. Tubular-shaped rods are the counterpart to the cones. The human eye has over 100 million rod cells.
The Mayans believed that cross-eyes were attractive and would make efforts to ensure their children became cross-eyed. They are sensitive to light levels and help give us good vision in low light. Rhodopsin pigment in rod cells are very sensitive to light.
Cones are the otherhand are less sensitive to light but can distinguish light.
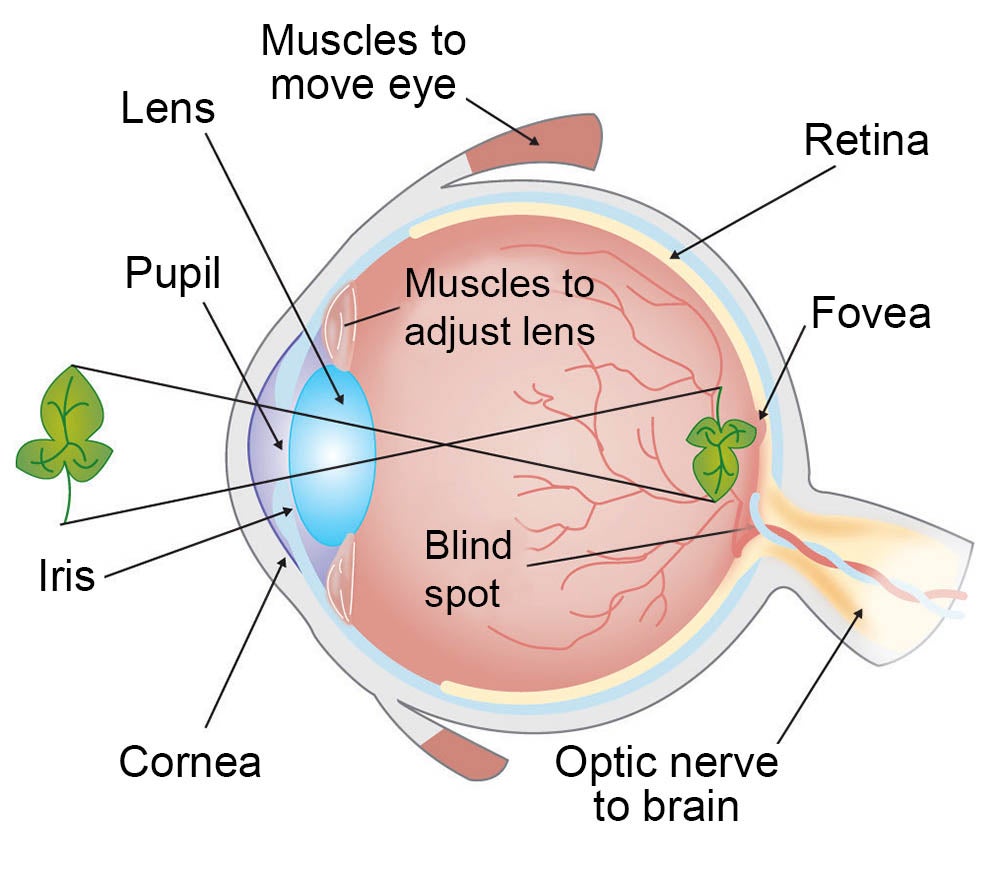
How Do We See Light Ask A Biologist
Rods American Academy Of Ophthalmology
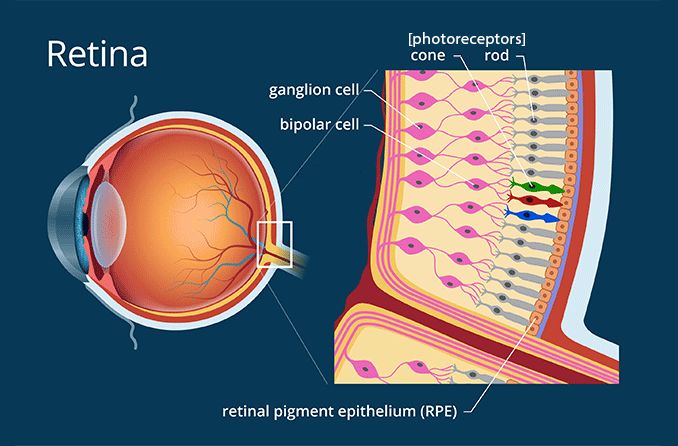
Photoreceptors All About Vision

The Eye Blue Cone Monochromacy



0 Response to "what do rods do in the eye"
Post a Comment